In early stages of biotherapeutic development, generic HCP ELISA are an easy-to-use solution to quantify HCP content in DS and show HCP clearance through the DSP. However, HCP quantification can be biased by the use of non-validated generic ELISAs. If generic ELISAs are used, it’s essential to validate their performance, including assessing dilutional linearity as well as 2D-DIBE coverage.
Key parameters to consider when assessing commercial HCP ELISA kits
Many commercial host cell protein kits (also called generic HCP ELISAs) are now available on the market. Although it’s easy to put together a shortlist based on the expression cell line (CHO, E.coli, Pichia pastoris…), choosing the single most appropriate kit for a specific bioprocess is less straightforward than most people believe.
The nature/concentration of the drug substance (DS) and the USP and DSP processes can highly affect the HCP expressed by the cell line during the bioprocess. In fact, how a generic HCP ELISA performs strongly depends on the two following critical reagents:
Anti-HCP antibodies used in the generic ELISA
An imbalance between some of the HCP produced during the bioprocess and the ELISA antibodies available for these HCP can lead to dilutional linearity concerns. As a result, the more you dilute your sample, the more the HCP concentration increases, leading to unreliable or even impossible quantification of the HCP in your sample.
Limited recognition of the bioprocess HCP by the antibodies from the ELISA is a huge concern since some HCP can be present in the DS, but not detected by the ELISA because of a lack of specific antibodies. It is consequently of the utmost importance to verify that the antibodies form the ELISA recognise as many HCP as possible, with an equal distribution across all of the bioprocess HCP population. This point is a regulatory requirement and is achieved through 2D-DIBE coverage assessment on large gels.
HCP standards
The HCP used as standard in ELISA kits are produced in a different way and at a different concentration than the HCP generated by the bioprocess. These differences in HCP populations lead to miss-quantification of the HCP in the bioprocess samples and DS because the calibration curve of the ELISA kit is not well adapted.
If these 2 critical reagents are not adapted to your bioprocess, an over-quantification or, most often and more risky, under-quantification of the HCP can easily be made with potential harmful effects on validation of the DSP protocol and on your whole project.
To select the most appropriate HCP ELISA kit for your bioprocess, we recommend that you compare the performance of 2 to 4 HCP ELISA kits for an optimal selection. After selection, you must validate the reliability of the antibodies from the generic ELISA through 2D-DIBE coverage assessment, and validate the HCP ELISA kit selected, in order to be fully aligned with the regulatory requirements.
Selection and suitability study of generic HCP ELISA kits
- Evaluation of the Dilutional Linearity on HCCF, in-process samples and DS
- Control of the LOD & LOQ
- Determination of the accuracy by spike recovery experiment on the DS. Ideally, this experiment should be carried out using the HCP issued from the bioprocess
- Verification of the specificity: absence of cross-reactivity with the DS
- Comparison of the HCP concentrations versus the total protein concentrations in the samples
- Comparison of the HCP pattern used as standard in the ELISA kit with the HCP from the bioprocess through 2D-DIGE
2D-DIBE Coverage assessment of anti-HCP antibodies from generic ELISA kits
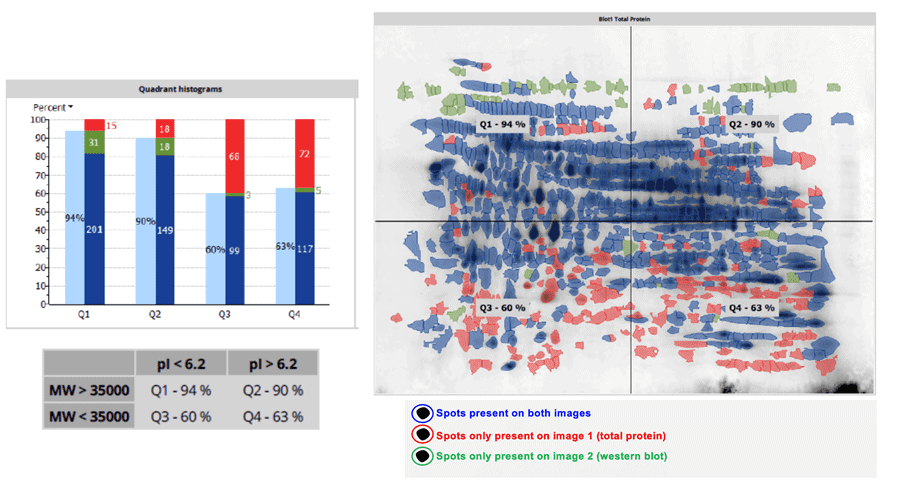
The determination of the percentage of coverage of the anti-HCP antibodies from the generic HCP ELISA over your process-specific HCP is made through 2 dimensional Western-Blot analysis (2D-DIBE). This coverage assessment is required by the FDA and EMA. Ideally, a coverage of > 70 % equally distributed over the 4 quadrants of the gel is required.
The 2D-DIBE coverage assessment requires specific expertise combined with state-of the art equipment:
- Optimised protocols for fluorochrome labelling of the HCP from the bioprocess
- Optimised 2D-DIBE protocols for generation of high-resolution HCP patterns using horizontal electrophoresis on large gels (20 x 25 cm)
- Optimised protocols for the determination of the western-blotting experimental conditions
- High-resolution scans of the membranes using the Typhoon RGB scanner
- Use of the Melanie 9 Software for spot detection, count and coverage determination. The results are expressed as total coverage percent and also as percent of coverage on each of the 4 quadrants of the membrane, as requested by the health authorities.
- After QA validation of the results, a report containing raw data (protocol, 2D SDS-PAGE and 2D-DIBE full resolution images & scans, Melanie9 detection & selection spot report), results and interpretation is available
ICHQ2R1 validation of the generic ELISA kit
If the generic ELISA is used for R&D purposes and bioprocess development (USP & DSP), the above-mentioned characterisations are sufficient to justify the use of a generic ELISA.
Once the generic ELISA kit is used for drug release testing for clinical phases, the authorities will require an ICHQ2R1 validation of the ELISA. If no generic ELISA is adapted to your production process, some fine-tuning of the generic ELISA can be performed to increase test reliability or, if not possible, you should consider developing a process-specific HCP ELISA kit.